When Is an Ip Address to the Client Confirmed in the Dhcp Process?
The server will quickly and automatically assign an IP address and some related network configuration parameters. Once the device has accepted the assignment, it can communicate with both the internal network and the public internet.
Relevant parameters
In addition to assigning IP addresses, these servers also provide relevant parameters, known as DHCP options. The Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA), the global coordinator of IP addresses, defines available DHCP parameters.
Options number in the hundreds. Key among them is how long the IP address can be used—known as the lease time. They also include the default gateway, its subnet mask, and its DNS server.
Some additional definitions
To clarify, let's quickly define some of these terms we just mentioned:
- A default gateway transfers data back and forth between the local network and the internet, or between local subnets.
- IP networking uses a subnet mask to separate the host address and the network address portions of an IP address.
- A DNS server resolves names to IP addresses, translating domain names that we easily remember, like bluecatnetworks.com, into IP addresses like 104.239.197.100.
Dynamic IP addressing with DHCP
The assignment of IP addresses happens dynamically within a given address range. As a result, a device connected to the network doesn't have a forever address. The IP address can periodically change as its lease time expires unless the lease is successfully renewed.
For services that always need to be on, a static IP address is often a better option. Corporate enterprises commonly use static IP addresses for hardware like mail servers. Certainly, a DHCP server should have a static IP address.
However, there are drawbacks to dedicating a specific IP address to a device or service. A network administrator must manually assign, configure, and track the IP address. It's a time-consuming task. Oftentimes, it requires the admin to physically be with the device.
Meanwhile, dynamic IP addresses are usually the preferred choice because they:
- Cost less to manage than static IP addresses;
- May offer more privacy and security with a constantly changing IP address; and
- Don't require manual administration when a device roams from one subnet to another.
DHCP communications protocol
Communications to fulfill a DHCP request involves both the server and client. Furthermore, a relay agent or IP helper often facilitates communication between the two. Relay agents receive broadcast DHCP messages from clients and then re-send those messages with configuration information to servers.
Communication happens via small units of data, called packets, that are routed through a network. Networking protocols like IP govern all its rules.
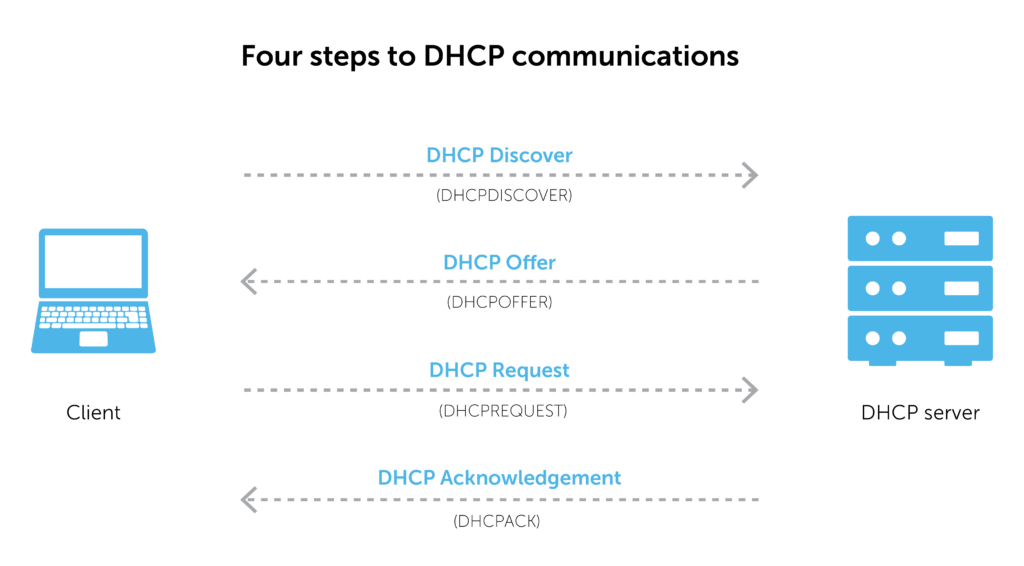
Most of the time, communication occurs in four steps. Briefly, they are:
- A discover packet is sent from the client to the server.
- The server replies to the client with a DHCP offer packet containing an IP address.
- The client receives and validates the offer, then sends a request packet back to the server to accept the address.
- The server sends an acknowledgement packet back to the client to confirm the chosen IP address.
With this in mind, one final point: DHCP alongside DNS and IP address management (IPAM) are together known as DDI. Want to know how to define DDI or how it works to form a complete management solution? The BlueCat platform is the place to start.
When Is an Ip Address to the Client Confirmed in the Dhcp Process?
Source: https://bluecatnetworks.com/glossary/what-is-dhcp/
0 Response to "When Is an Ip Address to the Client Confirmed in the Dhcp Process?"
Postar um comentário